

Czy wolisz polską wersję strony elektroda?
Nie, dziękuję Przekieruj mnie tam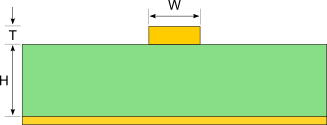
| Trace Width | W | ||
| Trace Thickness | T | ||
| Temperature Rise | Trise |
| Ambient Temperature | Tamb | ||
| Length | L |
First, calculate the area according to the following formula:
A = (T · W · 1.378 [mils/oz/ft2]) (I)
Then, calculate the maximum current:
IMAX = (k · TRISEb) · Ac (II)
Where:
A is the cross-section area [mils2] T is the trace thickness [oz/ft2] W is the trace width [mils] IMAX is the maximum current [A] TRISE is the maximum desired temperature rise [°C] k, b and c are constants. According to IPC-2221A Par. 6.2 (“Conductive Material Requirements”), their values for inner layers are as follows: k = 0.048 b = 0.44 c = 0.725
Equation (II) is based on a curve fit to the charts provided in [1] (par. 6.2, Figure B and Figure C).
The overall trace temperature can be calculated as follows
TTEMP = TRISE + TAMB
Where:
TTEMP is the trace temperature [°C] TRISE is the maximum desired temperature rise [°C] TAMB is the ambient temperature [°C]
First, convert the cross-section area from [mils2] to [cm2]:
A’ = A * 2.54 * 2.54 * 10-6
Then, calculate the resistance:
R = (ρ * L / A’) * (1 + α * (TTEMP – 25 °C))
Where:
T is the trace thickness [oz/ft2] W is the trace width [mils] R is the resistance [Ω] ρ is the resistivity parameter, whose value for copper is 1.7E-6 [Ω · cm] L is the trace length [cm] α is the resistivity temperature coefficient, whose value for copper is 3.9E-3 [1/°C] TTEMP is the trace temperature [°C]
Voltage drop can be calculated as follows:
VDROP = I * R
Where:
VDROP is the voltage drop [V] I is the maximum current [A] R is the resistance [Ω]
Power dissipation, or power loss, can be calculated according to the following formula:
PLOSS = R * I2
Where:
PLOSS is the power loss [W] R is the resistance [Ω] I is the maximum current [A]
Example 1
Inputs W = 12 mil T = 5 mil TRISE = 30 °C TAMB = 25 °C L = 12 inch
Output Cross-section Area = 60.00 mils2 IMAX = 4.17 A
Additional output Trace Temperature = 55 °C Resistance = 0.150 Ω Voltage Drop = 0.626 V Power Dissipation = 2.608 W
Example 2
Inputs W = 10 mil T = 3 oz/ft2 TRISE = 20 °C TAMB = 18 °C L = 25 cm
Output Cross-section Area = 41.34 mils2 IMAX = 2.66 A
Additional output Trace Temperature = 38 °C Resistance = 0.167 Ω Voltage Drop = 0.444 V Power Dissipation = 1.182 W
[1] IPC-2221A “Generic Standard on Printed Board Design”