Today, let's explain MOSFETs in the simplest way possible.
How to Identify the Three Terminals:
We know that MOSFETs have three terminals:
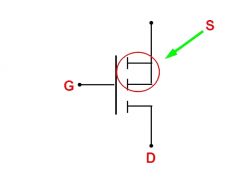
1. **Gate (G)**: The gate is the easiest to identify.
2. **Source (S)**: Whether it's a P-channel or an N-channel MOSFET, the intersecting lines indicate the source terminal.
3. **Drain (D)**: Regardless of the channel type, the side with the single lead is the drain terminal.
These three terminals are used to connect the external circuit.
G (Gate): Controls the MOSFET by changing the voltage level, which directly turns the MOSFET on or off.
D (Drain) and S (Source): These terminals function as the two ends of the switch circuit, one connected to the power supply and the other to ground.
How to Distinguish Between N-channel and P-channel:
It’s quite simple, just look at the symbol:
If the arrow points away from the gate, it's a P-channel MOSFET.
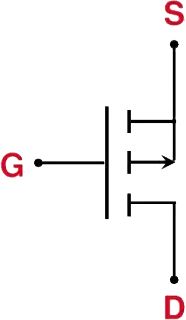
If the arrow points toward the gate, it's an N-channel MOSFET.
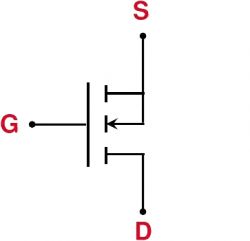
Direction of the Parasitic Diode:
If the arrow of the parasitic diode points from the source to the drain, it's an N-channel MOSFET.
If the arrow points from the drain to the source, it's a P-channel MOSFET.
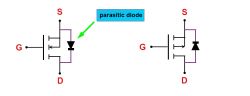
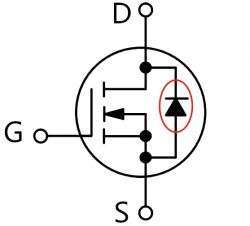
This parasitic diode plays a crucial role in circuit isolation. It helps in over-voltage protection by conducting excess current to the ground, preventing MOSFET damage. It also protects the MOSFET when the source and drain are reversed or when reverse-induced voltage occurs in the circuit.
Once you understand these basic principles, using MOSFETs becomes much simpler.


