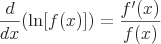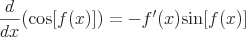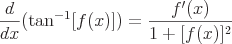Czy wolisz polską wersję strony elektroda?
Nie, dziękuję Przekieruj mnie tam
Definition of Limit
Right Hand Limit
Left Hand Limit
Limit at Infinity
Properties of Limits
Limit Eval. at +-Infinity
Limit Evaluation Methods
Continuous Functions
Continuous F&C.
Factor and Cancel
L'Hospital's Rule
Definition of a Derivative
Mean Value Theorem
Basic Properites
Product Rule
Quotient Rule
Power Rule
Chain Rule
Common Derivatives
Chain Rule Examples
The limit is a method of evaluating an expression as an argument approaches a value. This value can be any point on the number line and often limits are evaluated as an argument approaches infinity or minus infinity. The following expression states that as x approaches the value c the function approaches the value L.

The following expression states that as x approaches the value c and x > c the function approaches the value L.

The following expression states that as x approaches the value c and x < c the function approaches the value L.
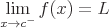
The following expression states that as x approaches infinity, the value c is a very large and positive number, the function approaches the value L.

Also the limit as x approaches negative infinity, the value of c is a very large and negative number, is expressed below.
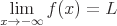
Given the following conditions:

The following properties exist:
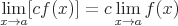


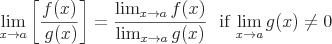
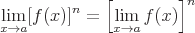





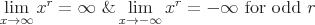
If f(x) is continuous at a then:
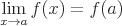
If f(x) is continuous at b:


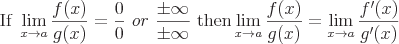
The derivative is way to define how an expressions output changes as the inputs change. Using limits the derivative is defined as:

This is a method to approximate the derivative. The function must be differentiable over the interval (a,b) and a < c < b.

If there exists a derivative for f(x) and g(x), and c and n are real numbers the following are true:

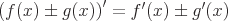

The product rule applies when differentiable functions are multiplied.
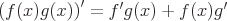
Quotient rule applies when differentiable functions are divided.

The power rule applies when a differentiable function is raised to a power.

The chain rule applies when a differentiable function is applied to another differentiable function.


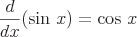




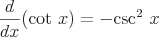

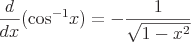

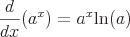

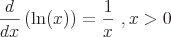
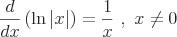

These are some examples of common derivatives that require the chain rule.