Selecting the Right Solar Panel Battery for Your Application
Solar panel batteries are used to store the energy produced by solar panels during the day. This energy is then used when the sun is not present, in the evening and at night. Different types of batteries are available on the market, each with their own characteristics and performance. We will show in this tutorial how to choose the right battery for your application with free and renewable energy.
The main characteristics of a battery
Purchasing a battery is by no means trivial and often requires the advice of experienced personnel. The cost is often quite high, and the user must optimize the expense according to the future uses of the accumulators. The main rule, in fact, is to get the most energy from them, at the same expense and footprint. The following characteristics should be considered when comparing and buying different types of batteries:
• Storage capacity: The storage capacity of a solar panel battery is determined by the amount of energy it can store. The higher the capacity, the greater the amount of energy that can be used when sunlight is not present.
• Life cycle: The life cycle of a battery is the number of times it can be charged and discharged before it is permanently replaced. Batteries with a longer life cycle may be more cost-effective in the long run.
• Lifetime: The lifetime of a battery is a different parameter from its life cycle and refers to the number of years it can be used before it is permanently replaced. Batteries with a longer lifetime cost more, but their advantages are appreciated in the long run.
• Technology: There are several technologies used in the market to build solar panel batteries, such as lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, lithium-ion (Li-ion) and others. Each of these technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to accurately analyze the different electrical applications to evaluate the most suitable model for one’s needs.
• Price: The price of a battery depends on all the parameters observed above, namely the technology used, the storage capacity and the durability. It is very important to evaluate the total cost of the battery, considering all these factors, to determine which option is the most affordable.
There is no absolute best battery, as each model has advantages and disadvantages. In addition, the specific needs of each user affect the performance of the batteries, so a battery that is reputed to be optimal for a certain application is not great for a different use. Therefore, it is advisable to make an accurate assessment of one’s needs and compare different models before choosing the most suitable battery. For this purpose, it is essential to rely on a consultant in the field who can undoubtedly provide the right advice. Let us now examine some of the most important types of batteries.
Lead-acid batteries for PV systems
Lead-acid batteries are often used to store the energy produced by solar panels and are composed of lead plates and sulfuric acid, which provide a large storage capacity. They are also relatively inexpensive compared with Li-ion batteries; however, they do have some disadvantages.
Lead-acid batteries are heavy and voluminous, and rooftop installation could become an issue. Their lifetime is more limited than that of Li-ion batteries. They usually last for about seven years if well used, and after this period, they need to be replaced. It is interesting to simulate the behavior of a lead-acid battery for photovoltaic (PV) systems using complex SPICE models. Figure 1 shows the principal circuit diagram for discharging a lead-acid battery with a resistive load. The model battery has the following static characteristics:
• Capacity: 75 Ah
• Resistance: 0.06 Ω
• Nominal voltage: 12 V
The two graphs show the voltages at the ends of the battery in the time domain for a battery with initial charge at 100% (top graph) and for a battery with initial charge at 70% (bottom graph). The resistive loads connected to the battery have the following ohmic values:
• 0.16 Ω
• 0.4 Ω
• 0.6 Ω
• 1.2 Ω
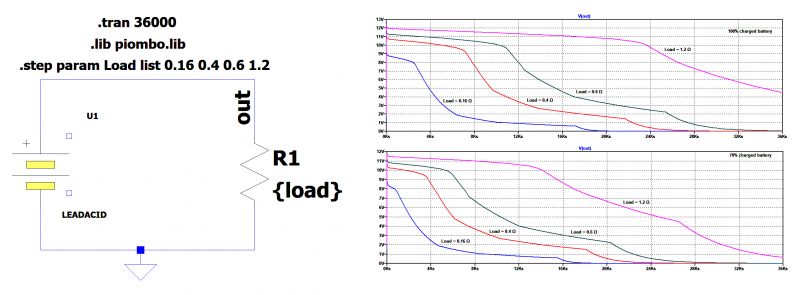
Figure 1: The discharge curves of a lead-acid battery under different loads, with initial charge of 100% and 70%, respectively
Li-ion batteries
Li-ion batteries are characterized by high energy density. They can store a large amount of energy in a relatively small volume. In addition, they are quite light and maintenance-free, making them ideal for installation in places with limited space. However, Li-ion batteries are much more expensive than lead-acid batteries. These batteries need a system for their proper management and control to ensure their smooth operation. If misused, in fact, they can be easily ruined.
Despite these disadvantages, Li-ion batteries are a reliable and promising option for the future, and if you have a sufficient budget, they can be an excellent choice for your PV system. Figure 2 shows the principal circuit diagram for discharging a Li-ion battery with a resistive load. The model battery has the following static characteristics:
• Capacity: 75 Ah
• Nominal voltage: 4 × 3.6-V cells, for a total of 14.4 V
The graphs show the voltages at the ends of the battery for a battery with 100% initial charge (top graph) and for a battery with 70% initial charge (bottom graph). The resistive loads connected to the battery, again, have the following ohmic values:
• 0.16 Ω
• 0.4 Ω
• 0.6 Ω
• 1.2 Ω
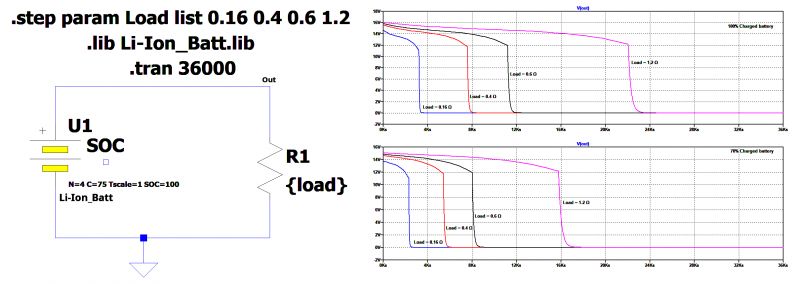
Figure 2: The discharge curves of a Li-ion battery with different loads, with initial charge of 100% and 70%, respectively
Conclusion
For PV systems, Li-ion batteries are usually considered a better choice than lead-acid batteries. The former has higher efficiency, and more energy can be stored per weight unit and volume than the latter. They also have a longer service life, with a higher number of charging cycles. Li-ion batteries also have a faster charge and discharge rate and can be charged and discharged more quickly. However, Li-ion batteries are usually more expensive than lead-acid batteries and require a more advanced management system to better manage their usage and lifetime.
To summarize, if one is looking for greater efficiency, durability, speed of charge and discharge and safety, Li-ion batteries may be a better choice for PV systems. Conversely, if you are looking for a cheaper solution, lead-acid batteries might be a good option.

Solar panel batteries are used to store the energy produced by solar panels during the day. This energy is then used when the sun is not present, in the evening and at night. Different types of batteries are available on the market, each with their own characteristics and performance. We will show in this tutorial how to choose the right battery for your application with free and renewable energy.
The main characteristics of a battery
Purchasing a battery is by no means trivial and often requires the advice of experienced personnel. The cost is often quite high, and the user must optimize the expense according to the future uses of the accumulators. The main rule, in fact, is to get the most energy from them, at the same expense and footprint. The following characteristics should be considered when comparing and buying different types of batteries:
• Storage capacity: The storage capacity of a solar panel battery is determined by the amount of energy it can store. The higher the capacity, the greater the amount of energy that can be used when sunlight is not present.
• Life cycle: The life cycle of a battery is the number of times it can be charged and discharged before it is permanently replaced. Batteries with a longer life cycle may be more cost-effective in the long run.
• Lifetime: The lifetime of a battery is a different parameter from its life cycle and refers to the number of years it can be used before it is permanently replaced. Batteries with a longer lifetime cost more, but their advantages are appreciated in the long run.
• Technology: There are several technologies used in the market to build solar panel batteries, such as lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, lithium-ion (Li-ion) and others. Each of these technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to accurately analyze the different electrical applications to evaluate the most suitable model for one’s needs.
• Price: The price of a battery depends on all the parameters observed above, namely the technology used, the storage capacity and the durability. It is very important to evaluate the total cost of the battery, considering all these factors, to determine which option is the most affordable.
There is no absolute best battery, as each model has advantages and disadvantages. In addition, the specific needs of each user affect the performance of the batteries, so a battery that is reputed to be optimal for a certain application is not great for a different use. Therefore, it is advisable to make an accurate assessment of one’s needs and compare different models before choosing the most suitable battery. For this purpose, it is essential to rely on a consultant in the field who can undoubtedly provide the right advice. Let us now examine some of the most important types of batteries.
Lead-acid batteries for PV systems
Lead-acid batteries are often used to store the energy produced by solar panels and are composed of lead plates and sulfuric acid, which provide a large storage capacity. They are also relatively inexpensive compared with Li-ion batteries; however, they do have some disadvantages.
Lead-acid batteries are heavy and voluminous, and rooftop installation could become an issue. Their lifetime is more limited than that of Li-ion batteries. They usually last for about seven years if well used, and after this period, they need to be replaced. It is interesting to simulate the behavior of a lead-acid battery for photovoltaic (PV) systems using complex SPICE models. Figure 1 shows the principal circuit diagram for discharging a lead-acid battery with a resistive load. The model battery has the following static characteristics:
• Capacity: 75 Ah
• Resistance: 0.06 Ω
• Nominal voltage: 12 V
The two graphs show the voltages at the ends of the battery in the time domain for a battery with initial charge at 100% (top graph) and for a battery with initial charge at 70% (bottom graph). The resistive loads connected to the battery have the following ohmic values:
• 0.16 Ω
• 0.4 Ω
• 0.6 Ω
• 1.2 Ω

Figure 1: The discharge curves of a lead-acid battery under different loads, with initial charge of 100% and 70%, respectively
Li-ion batteries
Li-ion batteries are characterized by high energy density. They can store a large amount of energy in a relatively small volume. In addition, they are quite light and maintenance-free, making them ideal for installation in places with limited space. However, Li-ion batteries are much more expensive than lead-acid batteries. These batteries need a system for their proper management and control to ensure their smooth operation. If misused, in fact, they can be easily ruined.
Despite these disadvantages, Li-ion batteries are a reliable and promising option for the future, and if you have a sufficient budget, they can be an excellent choice for your PV system. Figure 2 shows the principal circuit diagram for discharging a Li-ion battery with a resistive load. The model battery has the following static characteristics:
• Capacity: 75 Ah
• Nominal voltage: 4 × 3.6-V cells, for a total of 14.4 V
The graphs show the voltages at the ends of the battery for a battery with 100% initial charge (top graph) and for a battery with 70% initial charge (bottom graph). The resistive loads connected to the battery, again, have the following ohmic values:
• 0.16 Ω
• 0.4 Ω
• 0.6 Ω
• 1.2 Ω

Figure 2: The discharge curves of a Li-ion battery with different loads, with initial charge of 100% and 70%, respectively
Conclusion
For PV systems, Li-ion batteries are usually considered a better choice than lead-acid batteries. The former has higher efficiency, and more energy can be stored per weight unit and volume than the latter. They also have a longer service life, with a higher number of charging cycles. Li-ion batteries also have a faster charge and discharge rate and can be charged and discharged more quickly. However, Li-ion batteries are usually more expensive than lead-acid batteries and require a more advanced management system to better manage their usage and lifetime.
To summarize, if one is looking for greater efficiency, durability, speed of charge and discharge and safety, Li-ion batteries may be a better choice for PV systems. Conversely, if you are looking for a cheaper solution, lead-acid batteries might be a good option.



