Łukasz-O wrote: ...
I mean the very end of the installation, i.e. the one at the recipient - a socket with a pin, cross-section 2x 2.5mm2 in the TNC system. What is the name of the wire going to this socket that is not L?
In my opinion, N falls out because it cannot fulfill a protective function, PE also falls off because it cannot be working. So, for the bright narrow, what kind of cable is it? What name should I enter in the measurement protocol?
Col. Łukasz. What did you write down in the protocol?
If you entered PEN, you are in agreement with the theory contained in the book "Aparaty i electrical devices" - Gerhard Bartodziej Eugeniusz Kałuża. However (in my opinion) it is in contradiction with manufacturers of installation apparatus and accessories, installation designers and installers. The contradiction is due to the lack of connection terminals called PEN.
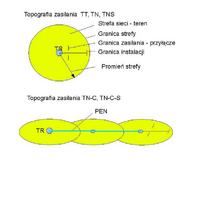
PEN is not part of the installation.
The wire from the socket through the N terminals of the electricity meter to the common point of the network is the N conductor. Permission to connect the N terminal with the PE terminal in the installation socket is an exception to the TN supply.
It is recommended (in new installations - required) to be powered by TNS, where PE is a separate conductor.
I wrote about PEN in previous posts, I would like to add that it is not a drawing line in a scientific drawing, but a circuit of serially connected quadruples, and even cascades, made of metallic and electrochemical conductors (Earth, soil). If the field conditions do not meet the standards, the elements RES, PER, ... are added.