FAQ
TL;DR: Windows 7 includes 5 recovery tools; "Use Startup Repair to fix certain problems." If F8 shows no "Repair your computer," boot from a Windows 7 installation or repair disc to access System Recovery Options. This FAQ helps Windows 7 users fix boot issues without the F8 entry. [System recovery options in Windows 7]
Why it matters: It restores unbootable systems without reinstalling or losing files.
Quick Facts
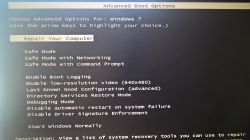
- F8 opens Advanced Boot Options before the Windows logo; “Repair your computer” appears only if recovery tools are installed. [*Advanced startup options (including safe mode)*]
- System Recovery Options provide five tools: Startup Repair, System Restore, System Image Recovery, Memory Diagnostic, and Command Prompt. [*System recovery options in Windows 7*]
- If “Repair your computer” is missing, boot from a Windows 7 installation disc or a System Repair Disc to reach the same tools. [*System recovery options in Windows 7*]
- A System Repair Disc must match 32‑bit or 64‑bit Windows and is created via Control Panel > Backup and Restore. [*Create a system repair disc*]
- DISM /RestoreHealth applies to Windows 8/10; for Windows 7 use SFC or offline servicing instead. [*Repair a Windows Image*]
Why is "Repair your computer" missing from F8 on my Windows 7 PC?
That menu entry appears only when recovery tools are installed on the PC. Custom installs or removed OEM recovery tools make it vanish. You can still access the same recovery environment by booting from a Windows 7 installation disc or a System Repair Disc. Press F8 only shows Safe Mode, Last Known Good Configuration, and related entries if recovery tools are absent. [Advanced startup options (including safe mode)]
How can I repair Windows 7 without that F8 entry?
Boot from a Windows 7 installation disc or a System Repair Disc. Choose your language, then select "Repair your computer" to open System Recovery Options. From there, run Startup Repair, System Restore, or open Command Prompt for advanced fixes. These tools are identical to the ones launched by the missing F8 option, so you lose nothing by booting from media. [System recovery options in Windows 7]
How do I open Advanced Boot Options correctly?
Restart the PC. Press F8 repeatedly right after the BIOS splash and before the Windows logo. If the Windows logo appears, restart and try again. Use a wired keyboard. Once the black Advanced Boot Options screen appears, pick Safe Mode, Last Known Good Configuration, or other entries as needed. [Advanced startup options (including safe mode)]
Should I try Last Known Good Configuration first?
Yes. It’s quick and non-destructive. It loads the most recent working driver and registry set. Microsoft describes it as starting Windows with the “last registry and driver configuration that worked.” It helps after a bad driver or registry change. If it fails, proceed with Startup Repair or System Restore. [Advanced startup options (including safe mode)]
How do I run Startup Repair if F8 "Repair your computer" is missing?
Use bootable media.
- Boot from a Windows 7 installation disc or System Repair Disc and click Repair your computer.
- Select the Windows installation and open System Recovery Options.
- Choose Startup Repair and let it complete; repeat once if prompted.
Startup Repair targets missing or damaged system files that block startup. [System recovery options in Windows 7]
Can I run sfc /scannow if Windows won’t boot?
Yes. Boot Safe Mode with Command Prompt, or boot from installation media and open Command Prompt. Run SFC online or offline: sfc /scannow for online, or sfc /scannow /offbootdir=C:\ /offwindir=C:\Windows for offline. SFC repairs corrupted system files and logs results to CBS.log. Run it until no integrity violations are reported. [Use the System File Checker tool to repair missing or corrupted system files]
Does DISM /RestoreHealth work on Windows 7?
No. The /RestoreHealth option applies to Windows 8.1/10 servicing. On Windows 7, use SFC to repair system files, or service an offline image with DISM without /RestoreHealth. If you need Windows component repair, consider an in-place upgrade repair using matching media instead. [Repair a Windows Image]
How do I fix BOOTMGR/BCD issues using Bootrec.exe?
Boot from a Windows 7 disc or repair disc. Open Command Prompt from System Recovery Options. Run: bootrec /fixmbr, then bootrec /fixboot, then bootrec /scanos, and finally bootrec /rebuildbcd. Reboot and test. This sequence rebuilds boot code and the BCD store that can prevent startup. Use only on the intended system drive. [How to use the Bootrec.exe tool in the Windows Recovery Environment to troubleshoot and repair startup issues]
F8 doesn’t work—what else can I do?
Timing matters. Press F8 before the Windows logo appears. If you see the logo, restart and try again. If the menu still won’t appear or recovery tools are missing, boot from a Windows 7 installation disc or a System Repair Disc to access System Recovery Options. [Advanced startup options (including safe mode)]
Which Safe Mode should I pick: networking or command prompt?
Windows 7 offers three Safe Mode variants: Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, and Safe Mode with Command Prompt. Choose Networking if you need internet or drivers for online troubleshooting. Choose Command Prompt to run tools like SFC without loading the full shell. Start with standard Safe Mode if unsure. [Advanced startup options (including safe mode)]
Can I create a System Repair Disc on another Windows 7 PC?
Yes. On a working Windows 7 machine, open Control Panel > Backup and Restore > Create a system repair disc. Use a blank CD/DVD. The disc must match the target system’s 32‑bit or 64‑bit architecture. Boot the problematic PC from this disc to reach System Recovery Options. [Create a system repair disc]
Which recovery tool should I run first inside System Recovery Options?
Start with Startup Repair. Microsoft says, “Use Startup Repair to fix certain problems.” If issues persist, try System Restore to roll back changes. Use Command Prompt for advanced commands like SFC or Bootrec. Memory Diagnostic helps when crashes suggest RAM faults. Pick System Image Recovery only if you have a recent image. [System recovery options in Windows 7]