Regularly, the contactor will be controlled by isolated begin and stop catches, and an assistant contact on the contactor is utilized, over the begin catch, as a hold in contact. I.e. the contactor is electrically hooked shut while the engine is working.
Rule of Direct On Line Starter (DOL)
To begin, the contactor is shut, applying full line voltage to the engine windings. The engine will draw a high inrush current for a brief span, the attractive field in the iron, and after that the present will be restricted to the Bolted Rotor Current of the engine. The engine will create Bolted Rotor Torque and start to quicken towards full speed.
As the engine quickens, the present will start to drop, yet won't drop altogether until the point that the engine is at a rapid, ordinarily about 85% of synchronous speed. The genuine beginning current bend is an element of the engine plan, and the terminal voltage, and is absolutely free of the engine stack.
The engine load will influence the time taken for the engine to quicken to full speed and in this manner the term of the high beginning current, yet not the greatness of the beginning current.
Given the torque created by the engine surpasses the heap torque at all velocities amid the begin cycle, the engine will achieve full speed. In the event that the torque conveyed by the engine is not exactly the torque of the heap at any speed amid the begin cycle, the engine will quits quickening. In the event that the beginning torque with a DOL starter is lacking for the heap, the engine must be supplanted with an engine which can build up a higher beginning torque.
The quickening torque is the torque created by the engine short the heap torque, and will change as the engine quickens because of the engine speed torque bend and the heap speed torque bend. The begin time is subject to the speeding up torque and the heap inactivity.
DOL beginning have a most extreme begin present and greatest begin torque.
This may cause an electrical issue with the supply, or it might cause a mechanical issue with the determined load. So this will be badly arranged for the clients of the supply line, dependably encounter a voltage drop when beginning an engine. In any case, if this engine is anything but a powerful one it doesn't influence much.
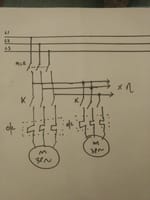
Parts of DOL Starters
Contactors and Loop
DOL part - Contactor
DOL part - Contactor
Attractive contactors are electromagnetically worked switches that give a protected and advantageous means for associating and interfering with branch circuits.
Attractive engine controllers utilize electromagnetic vitality for shutting switches. The electromagnet comprises of a loop of wire put on an iron center. At the point when a present course through the curl, the iron of the magnet ends up polarized, pulling in an iron bar called the armature. An intrusion of the present move through the curl of wire makes the armature drop out because of the nearness of an air hole in the attractive circuit.
Line-voltage attractive engine starters are electromechanical gadgets that give a protected, helpful, and practical methods for beginning and halting engines, and have the upside of being controlled remotely. The extraordinary greater part of engine controllers sold are of this sort.
Contactors are fundamentally used to control apparatus which utilizes electric engines. It comprises of a curl which associates with a voltage source. All the time for Single stage Engines, 230V curls are utilized and for three stage engines, 415V loops are utilized. The contactor has three fundamental NO contacts and lesser power evaluated contacts named as Assistant Contacts [NO and NC] utilized for the control circuit. A contact is leading metal parts which finishes or intrude on an electrical circuit.
NO-typically open
NC-typically shut
Over Load Transfer (Over-burden insurance)
Over-burden insurance for an electric engine is important to avert burnout and to guarantee most extreme working life.
Under any state of over-burden, an engine draws unnecessary current that causes overheating. Since engine winding protection disintegrates because of overheating, there are built up points of confinement on engine working temperatures to shield an engine from overheating. Over-burden transfers are utilized on an engine control to restrict the measure of current drawn.
The over-burden transfer does not give cut off. This is the capacity of over current defensive hardware like wires and circuit breakers, by and large situated in the disengaging switch fenced in area.
The perfect and most straightforward route for over-burden security for an engine is a component with current-detecting properties fundamentally the same as the warming bend of the engine which would act to open the engine circuit when full-stack current is surpassed. The task of the defensive gadget ought to be with the end goal that the engine is permitted to convey safe over-loads however is immediately expelled from the line when an over-burden has persevered too long.
Regularly melds are not intended to give over-burden security. Wire is ensuring against shortcircuits (over current security). Engines draw a high inrush current when beginning and customary circuits have no chance to get of recognizing this transitory and safe inrush current and a harming over-burden. Choice of Wire is rely upon engine full-stack current, would "blow" each time the engine is begun. Then again, if a breaker were picked sufficiently extensive to pass the beginning or inrush current, it would not ensure the engine against little, destructive over-burdens that may happen later.
The over-burden transfer is the core of engine insurance. It has opposite outing time qualities, allowing it to hold in amid the quickening time frame (when inrush current is drawn), yet giving insurance on little over-burdens over the full-stack current when the engine is running. Over-burden transfers are sustainable and can withstand rehashed excursion and reset cycles without need of substitution. Over-burden transfers can't, be that as it may, replace over current security hardware.
The over-burden hand-off comprises of a current-detecting unit associated in the line to the engine, in addition to a system, impelled by the detecting unit, which serves, straightforwardly or in a roundabout way, to break the circuit.