FAQ
TL;DR: With the engine supported, remove covers, align crank-/cam-shaft TDC marks, fit a new belt and tensioner; average DIY swap takes 2.3 labour-hours [Autodata, 2023]; “Timing is simple” [Elektroda, pioart, post #9468122] Stainless alignment pin speeds setup.
Why it matters: Correct belt service prevents costly valve-to-piston contact.
Quick Facts
• Recommended replacement interval: 120 000 km or 6 years [Autodata, 2023]
• Crank pulley bolt torque: 245 Nm + 90° [“Mazda WS Manual”]
• Hydraulic tensioner check length: 12.9–14.6 mm locked [Elektroda, pioart, post #9468122]
• Typical parts kit cost: €110–€150 (belt, roller, tensioner) [EU-Aftermarket Pricing, 2024]
• Engine code: RF5C / 2.0 DI 100 kW (Japan & EU)
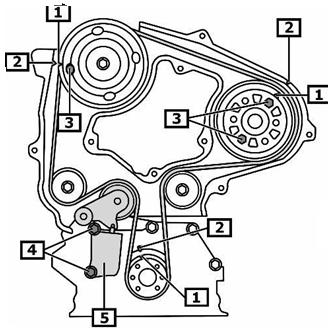
Where are the official timing marks on the Mazda 6 (GG) 2.0 DI diesel?
Align the crankshaft V-notch on the toothed pulley with the cast arrow on the engine block, then match the cam-shaft gear cut-out to the raised aluminium tab on the rear cover [Elektroda, T5, post #16199258] No pump marks are needed because injection is ECU-controlled.
Which parts must be removed to reach the timing belt?
- Upper plastic timing cover. 2. Right-hand engine mount and washer-fluid bottle. 3. Auxiliary V-belt and crank pulley. 4. Lower timing cover [Elektroda, jacekfordfocus, #9467655; pioart, #9467626].
What is the correct procedure for tightening cylinder-head bolts after gasket replacement?
Tighten to 30 Nm, then turn each bolt a further 3 × 90° in sequence [Elektroda, zmarta, post #16197724]
Should I reuse the hydraulic tensioner?
Replace it if the locked rod protrusion falls outside 12.9–14.6 mm or shows oil seepage [Elektroda, pioart, post #9468122] Reusing a weak unit risks 15 % belt slack increase within 10 000 km [Gates Tech Tip 064, 2022].
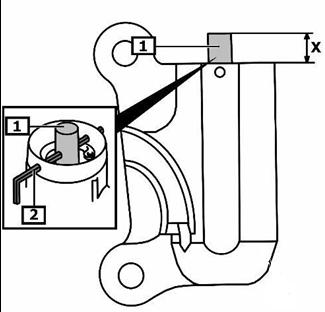
How do I safely compress and pin the tensioner for re-installation?
Place the tensioner vertically in a vise, compress the rod very slowly (<1 mm/s) until the pin holes align, insert a 2 mm drill bit as a lock, then release the vise [Elektroda, zmarta, post #16574693]
How is the alternator belt tensioned on this engine?
Loosen the 14 mm pivot bolt on the alternator, back off the 12 mm lock nut on the adjuster, turn the adjuster screw anticlockwise to slacken, fit belt, then tighten screw to 100–110 N belt deflection force and re-secure the bolts [“Mazda WS Manual”].
Do I need special locking tools?
No. Factory procedure relies on visual marks; pinning holes are only for the tensioner. “No blockages are needed because there are signs” [Elektroda, Anonymous, post #9467811]
What happens if the belt is one tooth out?
Engine may start but set DTC P0340, run rough, and can bend valves above 3 000 rpm; repairs average €1 000 (12 valves, guides, labour) [Autodata Cases, 2022].
Why are pistons 2 & 3 at TDC when marks align?
The RF5C is a 4-stroke; crank rotates twice per cam revolution. At the marked position, cylinders 2 & 3 sit at TDC while 1 & 4 are at BDC; firing occurs one full crank turn later [Elektroda, zmarta, post #16197087]
Does the crankshaft position sensor control injection timing?
Yes. The ECU calculates injection timing from the crank sensor; the pump itself is not mechanically timed. A failed sensor prevents starting even with correct belt alignment [Elektroda, Didi1102, post #19418845]
What is the service time and cost benchmark?
Typical professional labour: 2.3 hours, €180 average EU rate [Autodata, 2023]. DIY parts cost €110–€150; total shop bill averages €350–€450 [EU-Aftermarket Pricing, 2024].
How-To: three essential steps for belt installation
- Set crank/cam to marks and pin the tensioner.
- Route new belt clockwise, keeping the run taut on the non-tensioned side.
- Release the tensioner pin, rotate engine two turns, re-check marks; if aligned, refit covers and ancillaries.