Let’s start with the definition of SSH. It is an abbreviation of Secure Shell. It is the name of a cryptographic network protocol for secure data communication and executing remote operations between two networked computers, one of which is running an SSH server program and the other - SSH client program. SSH protocol provides a secure channel so that it prevents data from unwanted access by a third party. It can be used to gain access to SSH account on operating systems such as Windows 7 and 8 or Unix-like ones. The Secure Shell is most commonly used to log into a remote computer and execute commands.
By default, the port assigned to SSH servers is standard TCP 22 port. Of course, some circumstances may make you prefer to connect your SSH to another, non-standard port. To do this, you simply have to change the number of port the servers run on. Remember that the new port must be unused. Edit the SSH configuration file (…/etc/ssh). Once you are inside the file, replace port 22 with the number of port you want to use, then restart the sshd. When it is done, connection to the system cannot be established without changing the command by a client. To log in successfully, you should replace 22 port with the port that is actually used by SSH by using –p argument together with the new, previously specified number of port that is used instead of 22, to specify the port. Remember that connecting to port other than default 22 requires entering a password.
Connecting to a SSH is basically very easy, just download putty (if you haven't already got it) or another similar program, and set the connection like here below:
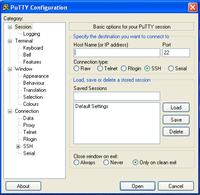
Just mark SSH, set the name of your host, and choose the port. After that, you can save your configuration for further use or just click Open to Connect to the host.
If you would like to have SSH on Windows, install OpenSSH – changing the port is made in OpenSSHetcsshd_config. Just change “#Port 22” to your own port like 23 and remove # - “Port 23”.
By default, the port assigned to SSH servers is standard TCP 22 port. Of course, some circumstances may make you prefer to connect your SSH to another, non-standard port. To do this, you simply have to change the number of port the servers run on. Remember that the new port must be unused. Edit the SSH configuration file (…/etc/ssh). Once you are inside the file, replace port 22 with the number of port you want to use, then restart the sshd. When it is done, connection to the system cannot be established without changing the command by a client. To log in successfully, you should replace 22 port with the port that is actually used by SSH by using –p argument together with the new, previously specified number of port that is used instead of 22, to specify the port. Remember that connecting to port other than default 22 requires entering a password.
Connecting to a SSH is basically very easy, just download putty (if you haven't already got it) or another similar program, and set the connection like here below:

Just mark SSH, set the name of your host, and choose the port. After that, you can save your configuration for further use or just click Open to Connect to the host.
If you would like to have SSH on Windows, install OpenSSH – changing the port is made in OpenSSHetcsshd_config. Just change “#Port 22” to your own port like 23 and remove # - “Port 23”.


