In this guide we will discuss some basic types of detectors.
Information on how to connect the detector to the control panel can be found in this guide:
Connecting any detector to any control panel - guide
MOTION DETECTORS
 PIR motion detector
PIR motion detector
(Passive Infra Red) is a passive infrared detector. Detection in it is caused by a pyroelement that reacts to changes in the radiation reaching it. It boils down to the detector reacting to objects moving in its detection field with a different temperature than the ambient temperature. Most detectors are equipped with wide-angle optics (around 90 °) and their effective range is within 10-15 m.
Infrared detectors are most often found in wall cases adapted for flat mounting or in a corner. For most detectors you can also buy or have special mounting brackets. Detectors adapted for ceiling mounting with 360 ° field of view are also available on the market. This is e.g. the Satel Aqua Ring detector.
The PIR detector is most effective when detecting objects moving perpendicular to its "beams".
Dual motion detectors PIR and MW
Dual PIR (Passive Infra Red) + MW (Micro Wave) detectors are actually PIR detectors with a microwave sensor using electromagnetic waves, i.e. the Doppler effect. The sensor is equipped with a transmitter and a receiver. Sent waves of appropriate frequency are received by the receiver. In the case of reflection of waves from a moving object, there is a change in frequency, which is recognized as an alarm criterion. I explain to customers that the "microwave" checks if "something" that "PIR" has "body" or whether it was just a breeze. Dual detectors due to the use of a double alarm criterion are much more resistant to false alarms than PIR detectors. Most often they are used in rooms where we can expect air movement. In practice, they are e.g. garages, rooms with air-conditioning, fireplaces, halls, etc. There are also detectors on the market where you can choose OR logic next to AND logic. In practice, due to the too high risk of false alarms, this logic is used very rarely.
Microwave detectors can interfere with each other, therefore they should not be mounted in close proximity to each other.
Similar to PIR detectors, dual detectors are most often found in wall casings, often equipped with a suitable holder, and ceiling detectors with an omnidirectional lens.
Detectors with anti-masking function
Both PIR and PIR + MW motion detectors can be equipped with a system that detects its masking. If the detector is covered, it signals it at the additional output. In Satellite detectors this is the output described as WRN and e.g. in the Vidicon IX AM detector as R-AM .
Such detectors should be used everywhere (at least in selected places) where there is a risk of intentional or accidental blocking.
Detectors with approach zone protection
A standard detector with Fresnel optics only detects movement from a distance. She does not "see" what moves directly with her.

Sometimes, however, there is a need for the detector to "see" the movement directly below it or in its immediate vicinity (e.g. a detector placed very close to the entrance door to the building just above the keypad, to detect people trying to use this keypad). We can use detectors with Fresnel optics with an additional lens at the bottom of the detector, or detectors with so-called mirror optics.
The detector detection field seen from the side looks like this:
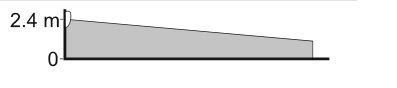
Examples of detectors with an approach zone implemented by an additional lens:
BOSCH ISC-BPR2-W12.
Examples of detectors with mirror optics:
Satel Ivory.
Curtain detectors
They differ from ordinary wide-angle motion detectors in reality with a lens. There are also detectors sold as standard on the market with a wide-angle lens, in which the lens can be replaced with a curtain. An example here is the VB curtain lens for Satel Aqua detectors.
There are also detectors on the market designed from the beginning to the end, including miniature ones to protect e.g. individual window recesses or doors. An example of such a detector can be, for example, the Paradox DG460 Paradoor.
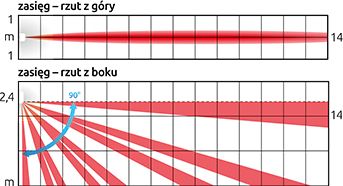
For example, the detection field of the Satel Agate curtain detector:
.................................................. ..........................
Advertisement
Also read:
Which GSM transmitter to work with the control panel? + Configuration examples.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with other guides, featured topics, articles on security systems such as intercoms, gate and barrier automation, alarm systems, cameras, access control:
Guides on security systems
If the above topics do not find the answer to your question, please visit the forum:
Security Systems
We also encourage you to visit the General Guides section, where you will find materials from other sections of the forum, including those starting their adventure with electronics:
General Guides
Information on how to connect the detector to the control panel can be found in this guide:
Connecting any detector to any control panel - guide
MOTION DETECTORS

(Passive Infra Red) is a passive infrared detector. Detection in it is caused by a pyroelement that reacts to changes in the radiation reaching it. It boils down to the detector reacting to objects moving in its detection field with a different temperature than the ambient temperature. Most detectors are equipped with wide-angle optics (around 90 °) and their effective range is within 10-15 m.
Infrared detectors are most often found in wall cases adapted for flat mounting or in a corner. For most detectors you can also buy or have special mounting brackets. Detectors adapted for ceiling mounting with 360 ° field of view are also available on the market. This is e.g. the Satel Aqua Ring detector.
The PIR detector is most effective when detecting objects moving perpendicular to its "beams".
Dual motion detectors PIR and MW
Dual PIR (Passive Infra Red) + MW (Micro Wave) detectors are actually PIR detectors with a microwave sensor using electromagnetic waves, i.e. the Doppler effect. The sensor is equipped with a transmitter and a receiver. Sent waves of appropriate frequency are received by the receiver. In the case of reflection of waves from a moving object, there is a change in frequency, which is recognized as an alarm criterion. I explain to customers that the "microwave" checks if "something" that "PIR" has "body" or whether it was just a breeze. Dual detectors due to the use of a double alarm criterion are much more resistant to false alarms than PIR detectors. Most often they are used in rooms where we can expect air movement. In practice, they are e.g. garages, rooms with air-conditioning, fireplaces, halls, etc. There are also detectors on the market where you can choose OR logic next to AND logic. In practice, due to the too high risk of false alarms, this logic is used very rarely.
Microwave detectors can interfere with each other, therefore they should not be mounted in close proximity to each other.
Similar to PIR detectors, dual detectors are most often found in wall casings, often equipped with a suitable holder, and ceiling detectors with an omnidirectional lens.
Detectors with anti-masking function
Both PIR and PIR + MW motion detectors can be equipped with a system that detects its masking. If the detector is covered, it signals it at the additional output. In Satellite detectors this is the output described as WRN and e.g. in the Vidicon IX AM detector as R-AM .
Such detectors should be used everywhere (at least in selected places) where there is a risk of intentional or accidental blocking.
Detectors with approach zone protection
A standard detector with Fresnel optics only detects movement from a distance. She does not "see" what moves directly with her.

Sometimes, however, there is a need for the detector to "see" the movement directly below it or in its immediate vicinity (e.g. a detector placed very close to the entrance door to the building just above the keypad, to detect people trying to use this keypad). We can use detectors with Fresnel optics with an additional lens at the bottom of the detector, or detectors with so-called mirror optics.
The detector detection field seen from the side looks like this:

Examples of detectors with an approach zone implemented by an additional lens:
BOSCH ISC-BPR2-W12.
Examples of detectors with mirror optics:
Satel Ivory.
Curtain detectors
They differ from ordinary wide-angle motion detectors in reality with a lens. There are also detectors sold as standard on the market with a wide-angle lens, in which the lens can be replaced with a curtain. An example here is the VB curtain lens for Satel Aqua detectors.
There are also detectors on the market designed from the beginning to the end, including miniature ones to protect e.g. individual window recesses or doors. An example of such a detector can be, for example, the Paradox DG460 Paradoor.
For example, the detection field of the Satel Agate curtain detector:

.................................................. ..........................
Advertisement
Also read:
Which GSM transmitter to work with the control panel? + Configuration examples.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with other guides, featured topics, articles on security systems such as intercoms, gate and barrier automation, alarm systems, cameras, access control:
Guides on security systems
If the above topics do not find the answer to your question, please visit the forum:
Security Systems
We also encourage you to visit the General Guides section, where you will find materials from other sections of the forum, including those starting their adventure with electronics:
General Guides




















