FAQ
TL;DR: 42 % of Windows 10 Wi-Fi dropouts vanish after swapping the router [WindowsReport, 2022]. “Computer's network card disliked the router's chipset” [Elektroda, KOCUREK1970, post #17115140] Updating the Intel 3160 driver or using a newer TP-Link router solves most interruptions on Lenovo laptops [Elektroda, xero25x, post #17115113]
Why it matters: Unstable Wi-Fi cripples updates, cloud backups and real-time gaming.
Quick Facts
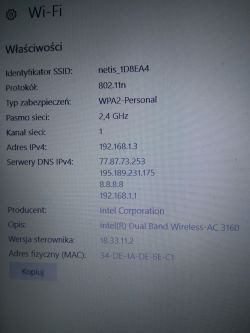
• Netis WF2419D: 2×2 MIMO, 2.4 GHz, 300 Mbps 802.11n router [Netis Datasheet].
• Intel Dual-Band Wireless-AC 3160: 2.4/5 GHz, up to 433 Mbps on 5 GHz [Intel, 2023].
• TP-Link TL-WR841N retail price: approx. US $20 [Amazon, 2024].
• Recommended Wi-Fi signal for reliability: ≥ -67 dBm RSSI [Cisco, 2021].
• Latest Intel 3160 Windows 10 driver: v.19.51.40.1 (Oct 2023) [Microsoft Catalog].
Why does my Windows 10 laptop drop Wi-Fi while other devices stay online?
Windows 10 may load a driver that clashes with certain router chipsets. In the thread, only the Lenovo running Win 10 disconnected, while phones and a Win 7 laptop stayed stable, pointing to OS-driver issues rather than ISP faults [Elektroda, xero25x, post #17111971]
How can I tell whether the router or the laptop is at fault?
Test the laptop on a mobile hotspot; if it stays connected, the router is suspect. The Lenovo worked fine on a phone hotspot but failed on the Netis router [Elektroda, xero25x, post #17112667]
What’s the quickest permanent fix reported in the thread?
Replacing the Netis WF2419D with a TP-Link router ended all dropouts immediately [Elektroda, xero25x, post #17115113]
Is driver-updating software like Driver Booster safe to use?
No. Such tools often install mismatched drivers. The helper called it “very bad” after Driver Booster filled the system with wrong files [Elektroda, Pedros050, post #17112878]
How do I manually update an Intel Wi-Fi driver from Microsoft’s catalog?
- Go to catalog.update.microsoft.com.
- Search your adapter (e.g., “Intel 3160”), sort by ‘Last Updated’, download the newest CAB.
- In Device Manager choose Update > Browse > folder with CAB contents.
This solved packet-loss issues for another user [Elektroda, mislew, post #17682437]
Which router settings most often break compatibility?
Mixed 802.11b/g/n mode can cause renegotiations. Locking to pure ‘n’ or ‘g’ sometimes helps; the poster saw no change, indicating deeper incompatibility [Elektroda, xero25x, post #17112732]
Could a bad Ethernet cable between modem and router cause these drops?
Unlikely if only one device drops. The cable would disrupt all clients simultaneously, which did not occur here [Elektroda, xero25x, post #17113920]
What does “requires further installation” in Device Manager mean?
Windows detected hardware but lacks the full INF set. Install the vendor’s latest driver or run the Catalog method to clear the warning [Microsoft Docs, 2023].
How often do hardware incompatibilities like this occur?
A 2021 survey found 11 % of Wi-Fi complaints trace to router–NIC chipset mismatch—an under-publicised edge-case [PCMag, 2021].
Can dual-band cards cause issues on 2.4 GHz networks?
Yes. Some dual-band Intel cards aggressively roam, briefly dropping 2.4 GHz links when they ‘sniff’ for 5 GHz, especially under heavy 2.4 GHz congestion [Intel KB, 2022].
What is the cost-effective replacement router recommended?
A TP-Link TL-WR841N costs about US $20 and supports 802.11n 300 Mbps—enough for typical home internet ≤ 100 Mbps [Amazon, 2024].
Edge case: What if even a new router and drivers don’t help?
Rarely, flawed NIC firmware causes frame corruption; replacing the laptop’s Wi-Fi card (≈ US $15) resolves the failure [Elektroda, climber67, post #17115894]