The PCM2912A, an outstanding audio codec crafted by Texas Instruments (TI), is equipped with a USB interface, mono microphone input, and stereo headphone output. It stands as an excellent option for novice enthusiasts in the sound card chip domain.
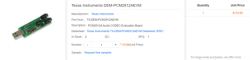
TI had introduced an evaluation module, the DEM-PCM2912AEVM, which, while functional, comes with a price tag of $110, making it a somewhat pricey affair. Additionally, the absence of a headphone amplifier limits its compatibility with high-quality headphones. Fear not, as we present a DIY alternative that might just be the solution you've been seeking.
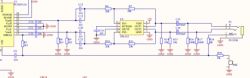
Overall Schematic Diagram
The USB sound card adopts the classic PCM2912A(Link)+TPA152 solution, with all circuits designed following the recommended circuit designs in the chip manuals.
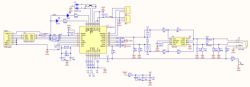
Detailed Design
Interface Design: Protecting and Optimizing Connections
The USB segment has been fortified with ESD protection and a fuse, serving as a shield against the perils of static electricity during the plugging and unplugging process. Meanwhile, the power input has been treated to a simple yet effective LC filter design. This not only ensures a pristine power input but also works wonders in enhancing the overall sound quality.
Crystal Selection: Precision in Frequency and Stability
Our choice of crystal, the NDK NX8045GB-6MHZ-STD-CSF-3, is housed in an 8mm x 4.5mm package. With a frequency of 6MHz and a temperature drift of 30ppm, it provides the stability and accuracy required for optimal audio performance.
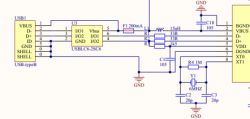
The microphone mute button, which doesn't see frequent use, has been enhanced with an SM05T1G for added ESD protection. To simplify things, tin-jump wires have been employed for power-saving and microphone gain settings. Since these adjustments aren't made on a regular basis, this approach offers a practical alternative to more complex jumper caps or DIP switches.
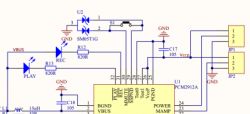
Power Amplifier Output and Headphone Interface:
The power amplifier section leans on the standard TPA152 (Link) circuit design. The output capacitors, in the form of tantalum electrolytic capacitors, have been carefully selected to ensure that the high-frequency equivalent series resistance (ESR) remains within an acceptable range.
The output interface is a stroke of genius, combining the microphone and headphone into a single unit. This design choice not only streamlines the setup but also ensures compatibility with the majority of mobile phone control headphones available in the market. For those seeking single-headphone use with microphone functionality, a dedicated microphone position has been reserved on the board, allowing for easy soldering of a microphone.
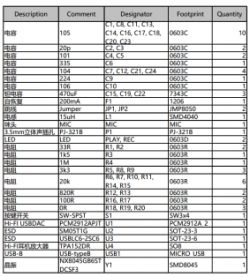
Bill of Materials
The components used are all relatively common and practical.
All these components can be conveniently found and purchased on the Unikeyic (Link)component platform, ensuring you have a reliable source for your DIY project.
Photo of the Physical Prototype
First Version: Bare PCB
The main chip generates a little heat during operation

The appearance after adding the casing: MicroUSB Version

The appearance after adding the casing: Type-C Version

Appearance:


TI had introduced an evaluation module, the DEM-PCM2912AEVM, which, while functional, comes with a price tag of $110, making it a somewhat pricey affair. Additionally, the absence of a headphone amplifier limits its compatibility with high-quality headphones. Fear not, as we present a DIY alternative that might just be the solution you've been seeking.
Overall Schematic Diagram
The USB sound card adopts the classic PCM2912A(Link)+TPA152 solution, with all circuits designed following the recommended circuit designs in the chip manuals.

Detailed Design
Interface Design: Protecting and Optimizing Connections
The USB segment has been fortified with ESD protection and a fuse, serving as a shield against the perils of static electricity during the plugging and unplugging process. Meanwhile, the power input has been treated to a simple yet effective LC filter design. This not only ensures a pristine power input but also works wonders in enhancing the overall sound quality.
Crystal Selection: Precision in Frequency and Stability
Our choice of crystal, the NDK NX8045GB-6MHZ-STD-CSF-3, is housed in an 8mm x 4.5mm package. With a frequency of 6MHz and a temperature drift of 30ppm, it provides the stability and accuracy required for optimal audio performance.

The microphone mute button, which doesn't see frequent use, has been enhanced with an SM05T1G for added ESD protection. To simplify things, tin-jump wires have been employed for power-saving and microphone gain settings. Since these adjustments aren't made on a regular basis, this approach offers a practical alternative to more complex jumper caps or DIP switches.

Power Amplifier Output and Headphone Interface:
The power amplifier section leans on the standard TPA152 (Link) circuit design. The output capacitors, in the form of tantalum electrolytic capacitors, have been carefully selected to ensure that the high-frequency equivalent series resistance (ESR) remains within an acceptable range.
The output interface is a stroke of genius, combining the microphone and headphone into a single unit. This design choice not only streamlines the setup but also ensures compatibility with the majority of mobile phone control headphones available in the market. For those seeking single-headphone use with microphone functionality, a dedicated microphone position has been reserved on the board, allowing for easy soldering of a microphone.

Bill of Materials
The components used are all relatively common and practical.

All these components can be conveniently found and purchased on the Unikeyic (Link)component platform, ensuring you have a reliable source for your DIY project.
Photo of the Physical Prototype
First Version: Bare PCB
The main chip generates a little heat during operation

The appearance after adding the casing: MicroUSB Version

The appearance after adding the casing: Type-C Version

Appearance:



