Hello I have a Onkyo TX-SR602E (European model) that will not show any signs of life the standby light doesn't light up. I have checked all the fuses and they are fine.
Here's what I have checked
When plugged in:
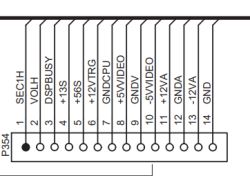
CPU VCC reads 4.7V at the firmware writing port (P701)
Display gets 5.5V
When unplugged:
CPU voltage drops to 3V
I think the CPU has a problem or the firmware is corrupted.
Background:
The last time I used the receiver was in 2022, and it worked fine.
It was stored in the basement for 2 years.
Before it went to the basement a factory reset was done.
I’ve replaced the super capacitor (C704).
I have the service manual for the receiver and the PDF for the Renesas M16C/62P (CPU).
Any help is very appreciated.
AI: When you plug in the receiver, do you hear any clicks from the main power relay or any other relays, or is it completely silent?
completely silent
AI: Have you checked for the presence of other voltages from the power supply, such as the main transformer secondary outputs or standby supply rails, and if so, what are their readings?
standby voltage is present 10 volts from the Transformer that is for standby power
Here's what I have checked
When plugged in:
CPU VCC reads 4.7V at the firmware writing port (P701)
Display gets 5.5V
When unplugged:
CPU voltage drops to 3V
I think the CPU has a problem or the firmware is corrupted.
Background:
The last time I used the receiver was in 2022, and it worked fine.
It was stored in the basement for 2 years.
Before it went to the basement a factory reset was done.
I’ve replaced the super capacitor (C704).
I have the service manual for the receiver and the PDF for the Renesas M16C/62P (CPU).
Any help is very appreciated.
AI: When you plug in the receiver, do you hear any clicks from the main power relay or any other relays, or is it completely silent?
completely silent
AI: Have you checked for the presence of other voltages from the power supply, such as the main transformer secondary outputs or standby supply rails, and if so, what are their readings?
standby voltage is present 10 volts from the Transformer that is for standby power