Hello everyone.
Today I wanted to demonstrate how to give the Anet A8 3D printer a new function in the form of a laser plotter.
I have described the whole project at http://resistor.pl/anet-a8-ploter-laserowy/
For this project you will need a laser that we can buy in China. It is important to pay attention to its power – lasers from 500mw to 15w are available, but the price of the latter oscillates around 800PLN.
I chose a laser with a power of 1W and a wavelength of 450nm, for which I paid around £175. The kit also included protective goggles and electronics responsible for the laser's correct operation.

Mounting
We mount the laser next to the printer head. The best way to do this is to use a printed mount. I have included several versions of the mount that can be found on the Thingiverse:
https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2571185
https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2117275
With three screws, we screw the laser to the printed piece, which then needs to be fixed in place of the print cooling fan (if you choose piece 1). Once the laser module is mounted, we connect the remaining electronics.

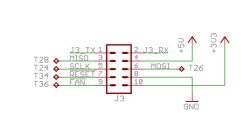
On the board responsible for the control we find four leads. Two of these are connected in turn to the laser diode itself and to the module's cooling fan. The other two sockets are TTL and 12V AC/DC. The 12V AC/DC lead is connected to the power supply cable, which will be used to supply the appropriate voltage to control the laser. We leave the TTL socket free, as we will not use it.
We connect a wire from 12V AC/DC to the main board of the 3D printer in place of the print cooling fan FAN2.

Calibrate the laser
We switch on and raise the Z axis to the level we have set.
We put on the protective goggles, go to the settings and turn on the print cooling to 1% or more in case the laser spot is not yet. visible.
Using the lens knob, we set the spot size to be as small as possible. This is best done on a white sheet of paper.
We zero the X and Y axes and then set them at point 0 of the printer table. We read the position of these axes, which will be our offset.
Operation and software
To operate the laser, we will use the free program Inkscape, which can be downloaded from: inkscape.org
We also download the plug-in for this program » Lokster’s Laser Engraving Inkscape Plugins
In the installed program, go to the Inkscape folder and extract the downloaded plug-in there.
Once this is done, we can create a graphic in Inkscape.
If we are using a pre-made image, we need to convert it into a vector graphic. To do this, we select Path in the menu and then the vectorise bimap option.
Select the finished graphic and choose Path/Object into Path
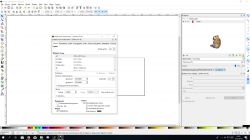
Now go to Effects/Lokster’s Tools and click on Laser Engraving. In the window that opens we adjust the settings for our plotter.
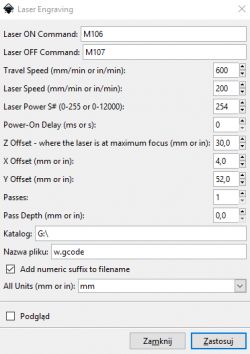
After indicating the save directory, name the file and click Apply. The gcode file saved in this way is uploaded to the memory card and run on the printer.
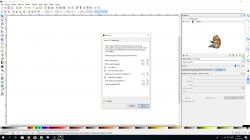
If you want your graphic to be hatched in the middle, you can use the Hatch fill option, which can be found by going to Effects/Lockster’s Tools.
With these settings we can adjust the hatching parameters of the interior of a given graphic.
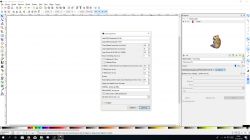
After applying the hatching options, we go to Laser Engraving and create a gcode file.
Change in printer software settings
The Anet A8 printer does not interpret the G2 and G3 commands corresponding to arcs. In order for the plotter to work correctly, it is necessary to edit the configuration_adv.h file in the SkyNet software. Enable the option as below (line approx.800).

After this correction we upload the software and can enjoy the new function of our printer.

Project description: http://resistor.pl/anet-a8-ploter-laserowy/
Laser control: http://lokspace.eu/anet-a8-3d-printer-laser-engraver-mod/
Cool? Ranking DIY