FAQ
TL;DR: Synaps THD‑2857 uses an ALi M3801 SoC with 4 MB SPI flash; “Let’s not throw away used equipment—check what we can use.” [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
Why it matters: This FAQ helps tinkerers, recyclers, and RF hobbyists repurpose DVB‑T boxes, extract firmware, and understand DVB‑T→DVB‑T2/HEVC implications.
Quick Facts
- CPU: ALi M3801 STB SoC; board also carries Samsung K4B1G1646G DDR3 SDRAM (1 Gb, 64M×16). [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
- Non-volatile: Winbond 25Q32FVSIG SPI Flash, 4 MB total firmware storage. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
- PSU: OB2536 controller; output 5 VDC at approx. 1.5–2 A; SB360 rectifier (3 A/60 V). [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
- Front panel: FD650S (TM1650S‑compatible) 4‑digit LED/keypad driver over I²C; IR receiver TSOP1338 at 38 kHz. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
- Chassis: steel shell with SCART on PSU board; space for 18650 cells after mainboard removal. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
What exactly is inside the Synaps THD‑2857 DVB‑T decoder?
It centers on an ALi M3801 SoC with 1 Gb Samsung K4B1G1646G DDR3 RAM. Firmware lives in a 4 MB Winbond 25Q32 SPI flash. The PSU uses an OB2536 controller, delivers 5 V at about 1.5–2 A, and rectifies with an SB360 diode. The front panel is driven by an FD650S (TM1650S‑compatible) over I²C, and IR input uses a TSOP1338 at 38 kHz. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
Can an old DVB‑T box be upgraded to DVB‑T2/HEVC by firmware?
Sometimes the main processor could decode HEVC if vendors enable it, but many designs rely on hardware decode blocks that software cannot replace. As one expert put it, “this cannot be bypassed with software.” Expect limited or no upgrade path on most DVB‑T‑only units. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19955197]
Will DVB‑T2 set‑top boxes work with older DVB‑T broadcasts?
Yes. DVB‑T2 tuners are backward compatible with DVB‑T, so one box can cover both during transition periods. This avoids double‑buying when multiplexes change standards regionally. [Elektroda, sq3evp, post #19956471]
How long did the DVB‑T→DVB‑T2/HEVC switch take in Poland?
User reports summarize a four‑phase migration set for March–June 2022, with completion targeted by June 30, 2022, varying by region. This helped explain why reception changed on different dates nationwide. [Elektroda, ladamaniac, post #19956846]
Were any DVB‑T multiplexes left on DVB‑T longer?
Yes. MUX‑3 (TVP) was noted as allowed to continue in DVB‑T until the end of 2023, extending compatibility for some viewers and delaying the need to upgrade. [Elektroda, Pan.Kropa, post #19955601]
Can I still use a DVB‑T box if I don’t need live TV anymore?
Many units, including the THD‑2857, can play media from USB to a monitor or TV. They remain useful as simple file players or IR‑driven front ends even after broadcast changes. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19955219]
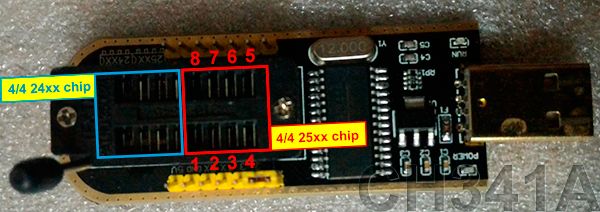
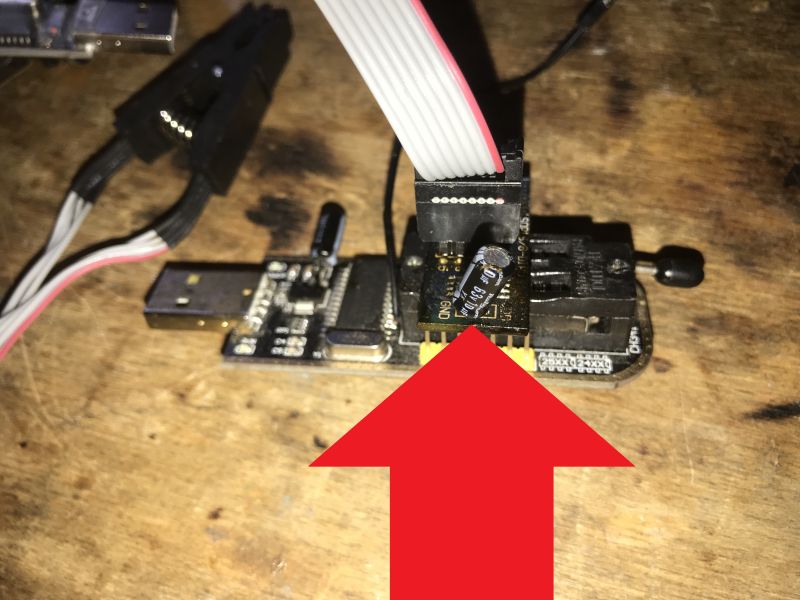
How do I dump the 4 MB SPI flash (Winbond 25Q32) with a CH341 programmer?
Three steps: 1) Attach an SOIC‑8 clip or socket adapter to the 25Q32, ensuring correct VCC and GND. 2) Read the full 4 MB twice and save both images. 3) Verify the header (e.g., NCRC bootloader) before any write. “Write may need a decoupling capacitor on VCC.” [Elektroda, p.kaczmarek2, post #21775592]
Why won’t my CH341 program the flash even though reading works?
Insufficient power stability is a common pitfall. Adding a capacitor across the target’s 3.3 V and GND often makes writes reliable. Clip contact quality and in‑circuit loads also affect success. “I have to add a capacitor on the power supply.” [Elektroda, p.kaczmarek2, post #21775592]
What is DVB‑T2 and what is HEVC?
DVB‑T2 is the second‑generation terrestrial TV standard, enabling higher capacity and robustness. HEVC (H.265) is the video codec used by many DVB‑T2 services for better compression than H.264, allowing more channels or higher quality in the same bandwidth. [Elektroda, ladamaniac, post #19956846]
How can I repurpose the THD‑2857 case and power supply safely?
The steel chassis is sturdy, and the PSU yields regulated 5 V at ~1.5–2 A. Add an RC snubber across the output rectifier to tame parasitics, as advised, and verify isolation gaps. Use proper bezels for the bright LED display. [Elektroda, żarówka rtęciowa, post #19954867]
Is an RC snubber really needed on the SMPS output?
Yes, for cleaner waveforms when transformer leakage inductance rings. A resistor‑capacitor cell in parallel with the rectifier diode suppresses oscillations. Select values by oscilloscope during load steps for best results. [Elektroda, żarówka rtęciowa, post #19954867]
What does the FD650S front‑panel chip do?
It is a TM1650S‑compatible LED/keypad driver. It handles four seven‑segment digits and up to 28 keys via I²C. This lets you keep the original display and buttons in DIY projects without extra microcontroller GPIO. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
What IR receiver does the front panel use?
The board uses a Vishay TSOP1338 module tuned to a 38 kHz carrier. That frequency matches most consumer remotes, so reuse is straightforward. Quote: “The receiver operates at 38kHz (IR carrier).” [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
Are there compact alternatives if I need a new tuner?
Yes. Users noted very small HDMI stick‑style DVB‑T2 receivers and newer compact set‑top boxes that are much smaller than older models. These reduce clutter beneath TVs. [Elektroda, sq3evp, post #19966309]
Is there space for batteries to make a portable build?
Yes. With the mainboard removed, the enclosure has room for a couple of 18650 cells. Combine with the 5 V rail and front panel to create a battery‑backed gadget or meter. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19953750]
Any edge cases when reusing the PSU board?
Some boards omit the snubber even though pads exist, leading to ringing. Also note the thin PCB trace used as a fuse‑link. Verify load transients on a scope and add protection as needed. [Elektroda, ArturAVS, post #19954927]