FAQ
TL;DR: “−80 dB is the limit” for app‑stable Wi‑Fi; that’s a hard borderline. To fix a Sonoff Mini R2 that disappears from eWeLink, change your 2.4 GHz channel, reduce overlap, and improve placement. [Elektroda, Erbit, post #21326136]
Why it matters: This keeps your smart switch reliably controllable from the app while your automations keep running.
Quick Facts
- Target RSSI: aim ≥ −67 dBm at the switch; below −80 dBm is unstable for control. [“Wi‑Fi Signal Strength Requirements”]
- Use only 2.4 GHz channels 1, 6, or 11; they’re the three non‑overlapping choices. [“Channels 1, 6, and 11: Why They’re Important”]
- SONOFF MINI R2 supports 2.4 GHz 802.11 b/g/n only; it cannot join 5 GHz SSIDs. [“SONOFF MINIR2 - Two Way Smart Switch”]
- Check channel congestion with a Wi‑Fi analyzer and pick the least‑busy channel. [“How to Choose the Best Wi‑Fi Channel”]
- Single‑radio repeaters halve throughput; prefer wired APs or mesh with Ethernet backhaul. [“The Truth About Wi‑Fi Range Extenders”]
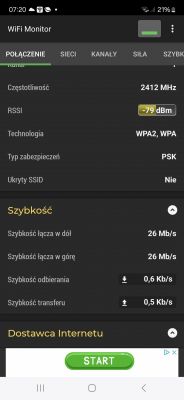
Is −79 dBm enough for a Sonoff Mini R2 to stay online?
It’s borderline. “−80 dB is the limit” for app‑reliable Wi‑Fi. Simple IoT can still pass tiny bursts, but app presence and manual toggles will drop intermittently at that level. Improve RSSI by changing channels and placement to restore stability. “IoT devices that transmit little data should work on such a weak signal.” [Elektroda, Erbit, post #21326136]
My channel graph shows many networks overlapping. What should I do?
Move your SSID to a less congested 2.4 GHz channel. Overlapping networks compete for airtime and cause dropouts. Shifting away from the busiest channels often stops the breaks in app visibility, especially at weak signal levels. [Elektroda, Erbit, post #21327758]
How do I change the 2.4 GHz channel on my Huawei router?
- Log in to the router’s admin page.
- Go to WLAN/Wi‑Fi settings, open 2.4 GHz Advanced, and locate Channel.
- Set a fixed channel (not Auto), save, and reboot if prompted.
This moves you out of the crowded channel range. [Elektroda, Erbit, post #21328223]
Which 2.4 GHz channel should I pick: 1/6/11 or 9?
Use channels 1, 6, or 11. They are the only non‑overlapping options in 2.4 GHz with 20 MHz width. Channel 9 overlaps adjacent channels and increases interference risk. Pick the least congested among 1, 6, or 11. [“Channels 1, 6, and 11: Why They’re Important”]
How do I measure Wi‑Fi signal right where the Mini R2 sits?
- Install a Wi‑Fi analyzer app on your phone.
- Hold the phone next to the switch box to read RSSI and channel.
- Screenshot the signal and channel view to compare after changes.
This shows the actual conditions the device sees. [Elektroda, Erbit, post #21325874]
Does a small plastic switchboard hurt Wi‑Fi?
Thin plastic adds minimal attenuation, but nearby wiring and any metal can disrupt or block signals. If the enclosure or surroundings include metal, expect much greater loss versus plastic or drywall. Relocating the device or antenna path can help. [“Wi‑Fi Signal Attenuation by Materials”]
Why do timers still run when the device looks offline in eWeLink?
eWeLink Schedule/Timer is stored on the device, so it can execute without continuous app connectivity. The app may show offline, yet scheduled actions still occur on time. [“eWeLink Help Center: Do timers work offline?”]
Should I add a repeater or move/add an access point instead?
Try channel optimization first. If signal remains weak, prefer a wired access point or a mesh node with Ethernet backhaul. Single‑radio repeaters typically halve throughput, which can worsen contention on crowded 2.4 GHz. [“The Truth About Wi‑Fi Range Extenders”]
What RSSI should I aim for at the switch?
Target −67 dBm or better at the Mini R2 for stable control. −70 dBm is a minimum for basic connectivity; below −80 dBm becomes unreliable for app presence and manual toggles. [“Wi‑Fi Signal Strength Requirements”]
Does Sonoff Mini R2 support 5 GHz, and could that cause pairing issues?
No. It supports only 2.4 GHz 802.11 b/g/n. Ensure your SSID offers 2.4 GHz and that the phone’s pairing process uses that band. If your router merges bands under one name, enable separate SSIDs or lock the 2.4 GHz during pairing. [“SONOFF MINIR2 - Two Way Smart Switch”]
How can I reduce interference from my solar inverter’s Wi‑Fi?
Place the inverter’s SSID on a different 2.4 GHz channel than your smart‑home SSID. Set channel width to 20 MHz to limit adjacent‑channel overlap. Avoid 40 MHz in 2.4 GHz; it stomps over neighbors and hurts reliability. [“40 MHz in 2.4 GHz Is Bad”]
Is 15 meters too far for 2.4 GHz indoors?
Distance alone isn’t decisive; obstacles and congestion dominate. Brick walls can add roughly 8–15 dB each, which, combined with busy channels, can push the link into dropout territory. Improve line‑of‑sight and channel selection to stabilize. [“Wi‑Fi Signal Attenuation by Materials”]