BU-808A: How to wake up a dormant Li-ion battery?
Subject:
This article provides information on why batteries can go to sleep and how to restore them to service.
Dormant battery
Li-ion batteries contain in their structure protective circuit which prevents them from being damaged in the event of over-discharge. This important element disconnects the link making it theoretically useless. After an extended period of time, the battery may go into sleep mode due to self-discharge, which is partly caused by the cell's chemical processes and partly by the battery protection circuitry constantly consuming a small current. Depending on the manufacturer, the protection circuit is activated at a voltage from 2.2V / cell to 2.9V / cell. (See also BU-802b: Elevated Self-discharge )
Waking up from sleep
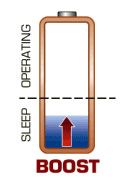
There are chargers that can wake a dormant battery by increasing its voltage in order to deactivate the protection system (boost). Chargers without this option detect the battery as damaged and will not charge the dormant battery. Wake-up is based on applying voltage to the battery contacts while limiting the current to a small level. In this way, the protection circuit receives power and the battery voltage can rise above the threshold above which normal charging begins. Typically the reviving process takes about a minute. If the cell voltage does not rise to the expected level then the cell should be considered damaged. Figure 1 shows in a simplified way what the wake-up procedure is.
Risk
Do not use this method on batteries whose voltage has fallen below 1.5V / cell and has remained at this level for a week or more. Copper bridges inside the cell can lead to a partial or complete short circuit. Charging such a battery can cause process instability, excessive heat generation, including the risk of fire. Advanced chargers can recognize such situations and stop the process of reviving a dormant cell.
Waking up the cell carries one more risk - polarity reversal. Most chargers can recognize a cell connected inversely, as long as there is voltage on its terminals. The dormant battery does not show any voltage at the terminals, so be very careful as there is a risk of connecting the battery upside down. In the absence of voltage, the charger may try to wake up the battery, but if the polarity is reversed, the cell will be permanently damaged. Li-ion cells are much more sensitive to polarity reversal than other types of batteries.
Sleep prevention
Storing lithium-ion batteries is not an easy topic at all. On the one hand, manufacturers recommend maintaining a state of charge in the range of 40% - 50% of the nominal value, but on the other hand, self-discharge of cells, especially at elevated temperatures, may cause excessive discharge and entering the sleep state. Knowing that the battery will not be charged for more than 12 months, it makes sense to increase the starting charge. (See also: BU-702: How to Store Batteries )
Tests
The Cadex laboratory tested 294 cell phone batteries that were returned under warranty. An advanced charger with an analyzer allowed to restore 91% of cells with a capacity of 80% and more. Deep dormant cells constituted 30% of the entire group. After recharging, they regained their working order. 9% of the batteries failed to wake up. All recovered packages have been returned to service and functioning without showing any defects. This case shows that there is a good chance of recovering a dormant battery.
Last updated on 2016.03.07
The article is a translation of the material contained on the website: BU-808a: How to Awaken a Sleeping Li-ion
Feel free to discuss the topic.
Marek
Subject:
This article provides information on why batteries can go to sleep and how to restore them to service.
Dormant battery
Li-ion batteries contain in their structure protective circuit which prevents them from being damaged in the event of over-discharge. This important element disconnects the link making it theoretically useless. After an extended period of time, the battery may go into sleep mode due to self-discharge, which is partly caused by the cell's chemical processes and partly by the battery protection circuitry constantly consuming a small current. Depending on the manufacturer, the protection circuit is activated at a voltage from 2.2V / cell to 2.9V / cell. (See also BU-802b: Elevated Self-discharge )
Waking up from sleep
There are chargers that can wake a dormant battery by increasing its voltage in order to deactivate the protection system (boost). Chargers without this option detect the battery as damaged and will not charge the dormant battery. Wake-up is based on applying voltage to the battery contacts while limiting the current to a small level. In this way, the protection circuit receives power and the battery voltage can rise above the threshold above which normal charging begins. Typically the reviving process takes about a minute. If the cell voltage does not rise to the expected level then the cell should be considered damaged. Figure 1 shows in a simplified way what the wake-up procedure is.
Risk
Do not use this method on batteries whose voltage has fallen below 1.5V / cell and has remained at this level for a week or more. Copper bridges inside the cell can lead to a partial or complete short circuit. Charging such a battery can cause process instability, excessive heat generation, including the risk of fire. Advanced chargers can recognize such situations and stop the process of reviving a dormant cell.
Waking up the cell carries one more risk - polarity reversal. Most chargers can recognize a cell connected inversely, as long as there is voltage on its terminals. The dormant battery does not show any voltage at the terminals, so be very careful as there is a risk of connecting the battery upside down. In the absence of voltage, the charger may try to wake up the battery, but if the polarity is reversed, the cell will be permanently damaged. Li-ion cells are much more sensitive to polarity reversal than other types of batteries.
Sleep prevention
Storing lithium-ion batteries is not an easy topic at all. On the one hand, manufacturers recommend maintaining a state of charge in the range of 40% - 50% of the nominal value, but on the other hand, self-discharge of cells, especially at elevated temperatures, may cause excessive discharge and entering the sleep state. Knowing that the battery will not be charged for more than 12 months, it makes sense to increase the starting charge. (See also: BU-702: How to Store Batteries )
Tests
The Cadex laboratory tested 294 cell phone batteries that were returned under warranty. An advanced charger with an analyzer allowed to restore 91% of cells with a capacity of 80% and more. Deep dormant cells constituted 30% of the entire group. After recharging, they regained their working order. 9% of the batteries failed to wake up. All recovered packages have been returned to service and functioning without showing any defects. This case shows that there is a good chance of recovering a dormant battery.
Last updated on 2016.03.07
The article is a translation of the material contained on the website: BU-808a: How to Awaken a Sleeping Li-ion
Feel free to discuss the topic.
Marek
Cool? Ranking DIY