

Delivered in a tasteful tin box. The inside is lined with a tightly fitted sponge, so you have to pull a little to get it out of the box.
The tester comes in two versions: UM24 without Bluetooth interface and UM24C with Bluetooth. The difference in the bottom PCB, where or not the Bluetooth interface is soldered.

The meter itself is quite an interesting design with a few unique features, especially one. It is the measurement of the power cable resistance. And the ability to control its functions from a smartphone, of course also from a computer.
The meter has a color display with a diagonal of 1.44 '.
Its measuring range is 4.50-24.0V / 0.00A-3.00A.
The resolution is 0.01V and the accuracy class is 1%.
When connected to the power supply with any button pressed, we enter the menu, in which we can set the Chinese or English language and reset its settings. Nothing fancy so it's not there.
However, an interesting feature is that the displayed image can be turned every 90 ° so that the measurement results are most conveniently read.

In each screen there is a "Help" button and there we get instructions what each button can do on a given screen. A distinction is made between a short press and a long press. Help available in the selected language.
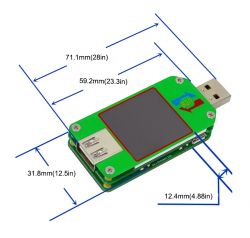
The exact dimensions are available in this picture.
However, the available information screens without the help menu are shown below.
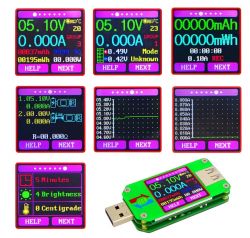
As you can see - the first one measures the voltage, current, temperature of the device and the following calculated: capacity in mAh, energy in mWh, current power in W and load resistance.
The device has 10 memory cells in which we can view the results of previously made measurements: groups 0-9 menu.
On the second screen, in addition to voltage, current and temperature, we have the voltage on the D + and D- cores and the recognized fast charging mode, if, of course, the charger provides one.
On the third screen, we have capacity, work and time.
Another interesting feature is the ability to set the load from which the meter is to record parameters. This is a nice option that allows you not to count the cable connected to the output of the device (some have resistors and take a little current) or to eliminate the idle run of the powerbank, which uses some electricity for indicators and its electronics without charging the battery anymore.
Another interesting fact on the fourth screen - measurement of the resistance and voltage drop of the connecting cable. Here we can check what quality cable we have. It is worth comparing the difference between the factory cable and the non-original one. The differences are sometimes colossal, so we will not be surprised why the phone is so slow to charge on this cable. This is quite a unique feature.
It is true that I managed in a different way without it and I had information about the quality of the cable, but here the manufacturer gave such a cymes and praise him for it.
The fifth and sixth screens use the capabilities of the graphic screen and we have a voltage and current graph.
On the last screen, we can set the timeoutscreen (unfortunately consumes some electricity, so its lighting falsifies the results of measuring the powerbank's capacity), the brightness level and the temperature display in C or F.
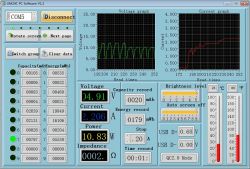
And now the most important highlight of the program - the Bluetooth interface. With its help, we can read and log measurement data on the computer. This is what the program looks like, which is additionally paid:
As well as recently, a program for Android and iOS has been available that allows you to view the parameters and control the meter.
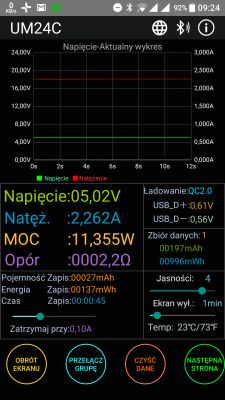
As you can see, this is the Polish language version. The project is free and will be developed.
This is how it can be seen on the meter screen:

I would like to add that the BT version has a red LED on the side, which flashes when the device is not connected and lights up permanently when connected. At this point, the device's screen is also turned on.
Current consumption with screen on and off.


Consumption is slightly lower without Bluetooth interface.
And an example of the help menu.



And here after flipping the screen.

In the background, you can see a candidate for the next article. This is by the way.
The current consumption with the screen off varies 0.069-0.085W, with the switched on from 0.135-0.155W.
In line with the blinking of the BT diode. After establishing a connection, the consumption increases by 0.02-0.08W.
Cool? Ranking DIY







